合成數據如何增強信用預測s
紫式晦澀每日一篇文章第40天
前言
-
今天是2022年第39天, 全年第6週, 二月的第2個週二. 今天來思考合成數據在「信用預測(Credit Prediction)」的層面上有何幫助.
-
今天的素材主要來自文章:
- 2020: Enhanced Credit Prediction Using Artificial Data
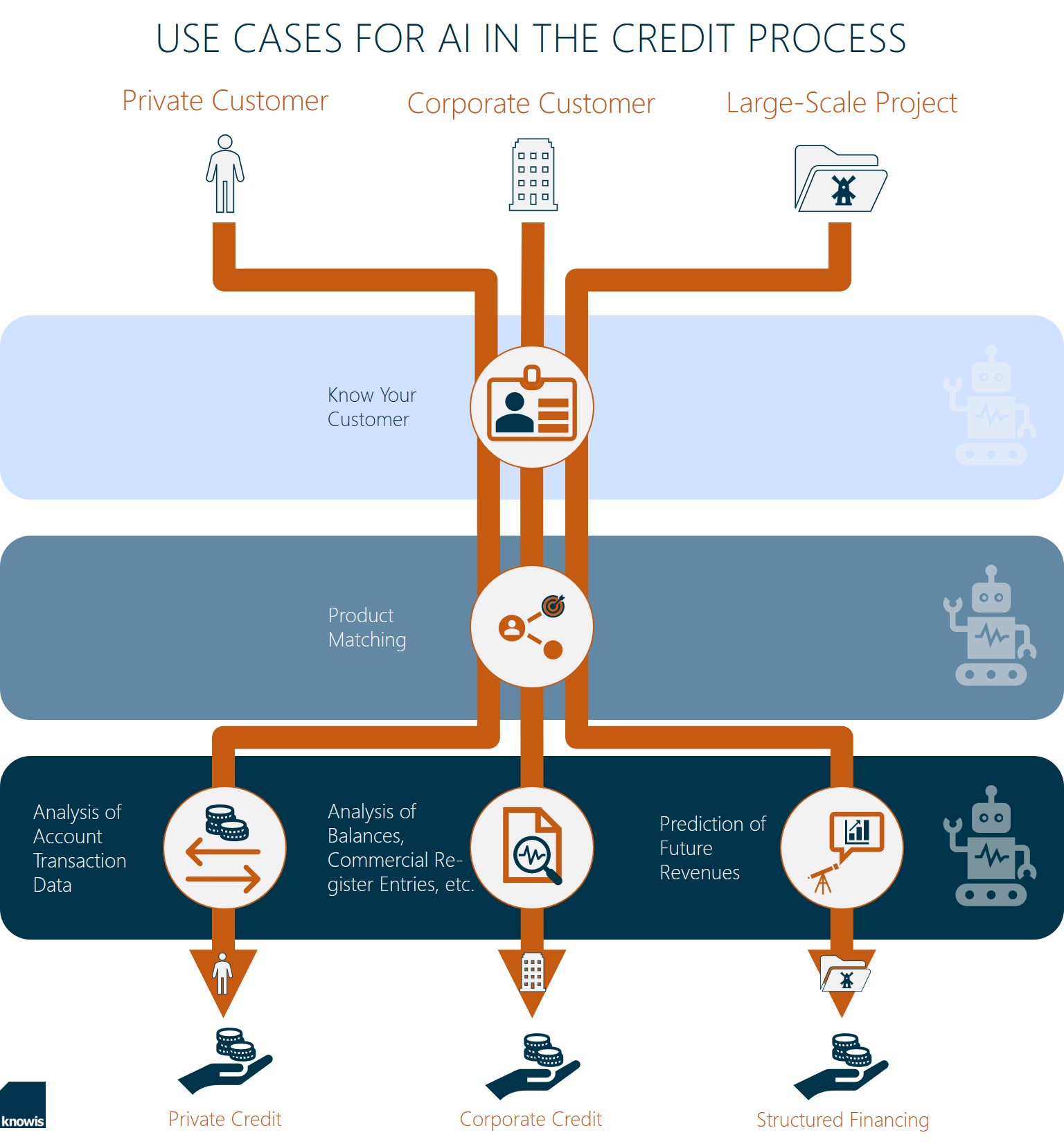
- SMARTER CREDIT PROCESSES: USE CASES FOR AI IN BANKING : 圖片來源
摘要
摘要:
- 用神經網路分析信用數據改良預測成功率.
- 用合成數據可對「成功率」有「邊緣改良(Marginal Improvement)」
- 人造數據: 確定訓練數據中各特徵的經驗機率分佈, 以抽取隨機樣本
- 對於「違約」與「不違約」, 不再受非均衡數據所擾, 兩類可以產生相同數量集的資料.
- 實驗方法使用「耦合(Copula)」以保留「原數據集的共變結構(Correlation structure of the original data)」, 接了優化特徵權重, 以達可接受結果.
- 結果顯示, 常見outcome的預測正確率有上升, 而AUC度量的上升是更顯著.
- 討論: 此結果在信用價值評估上的應用
AUC metric是否在實務上意義更大?
Abstract. Analysing credit data using a neural network has hitherto proved to be very resilient to attempts to improve success rates in prediction. We present a technique using simulated data which results in a marginal improvement in success rate. The empirical probability distribution for each feature of the training data is determined, and random samples are drawn from those distributions. The result is termed ‘artificial’ data. It is then possible to generate equal volumes of data for each of the binary outcomes (default or not), thereby alleviating a class imbalance classification problem. The simulation method uses a copula (to preserve the correlation structure of the original data) and optimal feature weighting to give acceptable results. The results indicate that overall percentage success rates for the more common outcome only are improved, but there is a more significant improvement in the AUC metric. The significance of this result in the context of assessing credit worthiness is discussed.
Keywords: Artificial data - 耦合(Copula) - Importance weight - Neural network - Lorenz curve
概論
入門(4段)
定義「成功」的AI於預測正確率與AUC數值:醫療數據可以:
- 許多AI在「醫療診斷(Medical diagnose)」的成功
- 數據上: 預測正確度超過90%, AUC超過0.9.
信用資料:成功率沒醫療數據那麼高:
- 神經網路在信用資料, 還沒證明很成功, 常用羅吉斯迴歸分析.
- 根據Chabon, 其成功率不會超過74%. [14]提供這個現象的解釋
- 感覺上, 使用「信用價值(Credit worthiness)」似乎不是「未來付款成功(future success in repayment)」的指標.
合成數據方法: 機率新穎偵測(Probabilistic Novelty Detection):
- 本文章想改善神經網路方法在信用數據上的表現
- 使用PND法「機率新穎偵測(Probabilistic Novelty Detection)(來自[6]), 來製造人工數據
- 本文章利用人工數據當作研究方法, 來改良信用資料
合成數據方法: 機率新穎偵測(Probabilistic Novelty Detection)
術語:major & minor 結果:
- 由於是二分類問題, 兩個分類各自的真實數據大小不同
- 比較多的那一類叫做major outcome
- 比較少的那一類叫做minor outcome
文獻回顧(6段):信用風險&人造數據
新穎偵測&信用價值:
- 本文獻回顧集中在「新穎偵測(Novelty Detection)」的應用與「信用價值(Credit worthiness)」的評估.
- 分類一: AI with Credit Data: Previous Research
- 分類二: Summary of the Metric Framework for Data Concentration
- 分類三: Summary of Probabilistic Novelty Detection
分類一:AI信用資料:
- 早期AI科技應用到信用資料的結果, 沒有應用到醫療資料那麼耀眼.
- 在[12]中, 使用German credit data成功率是百分之77.7; 在[8]中, Australian creditdata是百分之88.1
- 這些成功率, 偽裝了「主要結果(major outcomes)」與「次要結果(minor outcomes)」
- 懷疑這些結果用了(1) behavioral indicator of default 或者 (2) loans只對被選出來特定的用戶with high probability of non-default.
之前好的結果, 可能是「特徵工程」後的結果.
分類二:度量資料集中的框架:
- 在[14]裡面, 研究了人工神經網路來建模「信用風險(Credit risk)」, 研究「相對失敗(relative lack of success)」
- 衡量「資料形狀」的三種度量: 耦合(Copula), 超球面(Hypersphere)與 K近鄰(K-Neighbours)
- 組合成單一度量$\hat{H}$. 此度量越高, 表示「資料太多噪音」或者「不充足預測資訊」來訓練神經網路.
- 資料的豐富度與複雜度, 來至導致成功或失敗的不同路徑, 因此已經沒什麼改良攻堅
- 相對於「主要結果」與「次要結果」的資料, 則表示巧合(???)
衡量「資料形狀」的三種度量: 耦合(Copula), 超球面(Hypersphere)與 K近鄰(K-Neighbours)
可以用度量$\hat{H}$評估訓練數據集的品質.
****:
****: ****:
****: ****:
****: ****:
方法

方法(1圖10段):人造數據製造與使用
****: ****: ****: ****: ****: ****:
結果

方法(7段): 耦合與重要性權衡
****: ****: ****: ****: ****: ****:
討論

討論(1圖3段): 分析羅倫茲曲線
****: ****: ****: ****: ****: ****:
結論(2段)
後記
本文章是很整齊的IMRD結構, 能快速找到研究結果, 是一個可以精通的輸出模板.
2022.02.07. 紫蕊 於 西拉法葉, 印第安納, 美國.
| Version | Date | Summary |
|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 2022-02-08 | 初次閱讀, 建立基本框架, 逐句讀故事. |
評論